
![]()
[Download PDF - 189KB]
Although the thirst for bandwidth seems unquenchable, carriers are reluctant to invest heavily in new infrastructure until they see returns on current services. Also, despite massive bandwidth increases on backbones, the last mile problem – getting fast, affordable, reliable data from the ISP to the subscriber - persists.
Most subscribers are resigned to the reality that a single broadband access service fails to meet their needs. They cannot afford the premium services that are within reach of large corporations and often these are only available in limited areas. What if a service provider could make superior performance broadband services available to the customer by using existing carrier services? This is the potential that Multilink-IP (ML-IP) delivers.
ML-IP boosts your broadband revenue by enabling you to provide differentiated subscriber services that enhance the speed and reliability of any IP capable carrier access service, with minimal capital investment by your organization. Any service provider can build upon xDSL, Cable, Frame Relay, Dedicated Lines, ISDN or PSTN access services to create solutions that cater to almost any business market and deliver faster, more reliable broadband access.
ML-IP is a patent-pending method designed by ePipe Pty Ltd. It combines the bandwidth of multiple broadband links between the customer and you to create a wider virtual pipe into your network. Unlike traffic load balancing or multi-homing gateways, ML-IP creates fragments and transfers them across multiple links simultaneously. This ensures it uses the full bandwidth of each link and delivers near linear speed increases as additional links are added. The fragments are combined at the provider and these are then forwarded to the Internet.
The broadband links can be spread across multiple backbones to provide high availability through link redundancy for the customer if one or more carriers incur an outage. Link loss detection, fallback and link reconnection occur automatically within seconds. In the case of major outages, ML-IP can also fail over to one or multiple bonded ISDN or PSTN dial backup links.
ML-IP lets you better service your current subscribers with a range of ‘custom branded’ broadband services. It also allows you to attract new subscribers who cannot upgrade to premium services because of their location (limited service reach). ML-IP enables you to deliver premium services to a wide range of subscribers because of its wide reach (any broadband service) and affordability (building on multiples of a common, cost-effective service).
ML-IP presents a unique revenue generating opportunity for service providers because: -
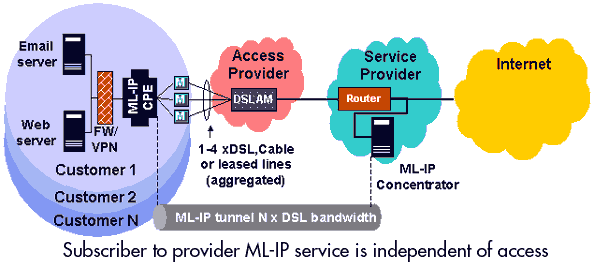
With an ML-IP-powered network, your organization can offer subscribers superior services without having to invest in expensive DSLAMs, switches or aggregation edge routers. As ML-IP is a ‘layer 3’ multilink scheme it can aggregate multiple links at each subscriber and terminate them at a single high-speed access point within the provider network. This eliminates the one-to-one port ratio required by other techniques such as inverse multiplexing (IMA) and Multilink PPP (ML-PPP). The packet fragmentation, sequencing and aggregation are completely independent of the access technology.
Each subscriber requires a ML-IP capable CPE gateway that can aggregate multiple broadband links from access routers (DSL, cable, leased line) or bridging modems (ADSL). The following differentiated broadband access services can be offered quickly and easily.
While ADSL delivers high-speed Internet access over the existing narrowband
network, it falls far short of being able to deliver full services that include
video. Most subscribers that have access to ADSL are limited to the globally
standardized, interoperable, splitter-less service known as universal ADSL,
G.Lite or G.992.2. This is a more economical service that supports a maximum
of 1.5 Megabits/sec downstream and 512 Kilobits/sec upstream over standard
phone lines as long as the subscriber is located no more than 6 KM from the
carrier access points. In many regions, carriers limit the maximum upstream
of G.Lite to well below 512 KBPS in most cases it is more like 256 KBPS upstream.
In practice lower-cost fractional G.Lite services are also offered such as
512K/128K, 256K/64K.
Many small business subscribers may be satisfied with their newfound web surfing
bandwidth afforded by ADSL G.Lite services. However many are also changing
business practices to rely more heavily on the Internet and its services such
as e-mail, file transfer, e-commerce, VPNs, etc. This changes their data traffic
profile from mainly incoming (downloading, surfing, etc.) to outgoing (e-mail,
file transfer, remote access, etc.)
As businesses add remote workers through an Internet-based remote access VPN there will be even more traffic required to travel upstream through the ADSL connection. With 64K, 128K or 256K upstream at their disposal, a few remote workers or a temporary remote office will easily consume available upstream bandwidth and adversely affect performance at the main office.
 These
subscribers most likely are not in a position to upgrade to a premium broadband
or private leased line service. However with an ML-IP CPE device, such as
the ePipe 2344 gateway, they can boost the upstream and downstream bandwidth
incrementally as needed to a provider that supports an ML-IP concentrator.
You can offer small business subscribers over 5 MBPS downstream and over 1.5
MBPS upstream on multiple G.Lite circuits. In addition you can offer many
bandwidth increments in between based on fractional G.Lite circuits (512K/128K,
etc.), which are available to more subscribers at a cost reflecting their
performance.
These
subscribers most likely are not in a position to upgrade to a premium broadband
or private leased line service. However with an ML-IP CPE device, such as
the ePipe 2344 gateway, they can boost the upstream and downstream bandwidth
incrementally as needed to a provider that supports an ML-IP concentrator.
You can offer small business subscribers over 5 MBPS downstream and over 1.5
MBPS upstream on multiple G.Lite circuits. In addition you can offer many
bandwidth increments in between based on fractional G.Lite circuits (512K/128K,
etc.), which are available to more subscribers at a cost reflecting their
performance.
Hosting a web or e-commerce server at the subscriber site is less than ideal with a standard or fractional G.Lite ADSL connection supporting 64K to 256K upstream. With ML-IP, subscribers can easily push more than 1.5 MBPS upstream to their customers, making it a viable solution.
Dedicated services for premium high-speed Internet access and interoffice
traffic are still very expensive and not always available to subscribers.
Generally fiber connections of various capacities are only available in certain
sections of the central business district. Symmetric DSL services provide
an excellent solution for those subscribers that will have substantial interoffice
traffic in addition to Internet access. In most cases the interoffice traffic
is transferred via a site-site VPN over a private IP, Frame Relay, or ATM
network, or the public Internet.
The recommended standardized symmetric DSL service for these applications
is known as Symmetric High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL or G.991.2)
and supports 2.3 MBPS upstream and downstream over one copper pair. These
DSL links do not support a standard phone connection on the same copper. G.SHDSL
is being deployed primarily for business customers, however 2.3 MBPS is insufficient
bandwidth for many of today's Internet-centric, distributed businesses.
With ML-IP CPE devices at the subscriber site and ML-IP in your network you can offer fractional fiber bandwidth over standard G.SHDSL circuits. Create business- grade symmetric broadband services supporting 4 to 8 MBPS upstream and downstream at a fraction of the cost of fiber connections with much wider availability. This level of bandwidth gives high-end subscribers the flexibility to host high-performance web and e-commerce servers on-site as well as the ability to introduce cost-effective video-conferencing.
With the bandwidth scalability afforded by ML-IP you can now offer ultra high-speed ADSL services for multi-tenant, campus and Internet café subscribers based on multiple full-rate ADSL services that are available through more specialized access providers. Some full rate ADSL services support 6M/640K with a maximum of 8M/1M at locations 4 to 6 KM from an access point.
You can actively pursue subscribers seeking ‘Very High Speed Digital Subscriber Line’ (VDSL or G.993) connections using multiple full-rate ADSL (G.DMT, G.992.1and ANSI T1.413 I2) circuits to deliver full services that include video. The VDSL standard is still in the definition phase so many specifications are still in flux. Generally it proposes 6.5M to 52M downstream and 1.8M to 6.4M upstream for the asymmetric service. However all proposals for this service impose a ridiculously short proximity, in the range of 0.3 to 1KM, between a subscriber and an access point for any VDSL speed increase above a full rate ADSL service. This means proposed VDSL services require expensive multiplexing equipment in the client building or in a street cabinet outside the building. In addition VDSL generates significant radio frequency interference and is also sensitive to external interference from broadcasters, both are slowing its real world adoption and deployment.
With ML-IP and standard full rate ADSL circuits, asymmetric VDSL speeds are possible today from the subscriber to your network without dedicated VDSL multiplexing equipment and without the distance restrictions or interference problems. ML-IP can be loaded onto Linux-based set-top boxes or small footprint PCs with multiple network ports creating a high-performance CPE gateway. You can easily offer VDSL speed broadband services ranging from 10M/1M way up to 25M/3.5M over multiple full-rate ADSL circuits to subscribers right now.
Your investment consists of a standard PC running Linux and ML-IP Concentrator software within your network to terminate the ML-IP links from many subscribers. Because ML-IP operates between the customer and the service provider, it is transparent to the carrier. It works across xDSL, Cable, Leased Lines, Frame Relay, etc., allowing the provider to offer a wide range of high-speed solutions up to fractional fiber speeds. One ML-IP concentrator can service up to 100 subscribers depending on the type of service you plan to provide. It connects to your main Internet router using a single fast Ethernet connection for terminating ML-IP links from subscribers and forwarding aggregated traffic to the Internet.
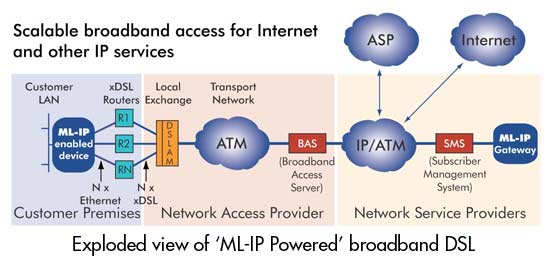
This simple combination allows you to offer ‘custom branded’ scalable multi-megabit broadband access without any support from the carrier for broadband link aggregation. Adding ML-IP to your network is the least capital-intensive method of offering subscribers incrementally scalable bandwidth across any access type. In addition your 'custom branded' service provides subscribers with high availability and the greatest coverage by boosting available broadband carrier services you already offer.
In order to make it simpler for you to evaluate the ML-IP proposition, ePipe has developed a free time-limited evaluation program; simply click on the link below for full details.
http://www.ml-ip.com/html/solutions/mlip-evaluate.html
Many service providers worldwide are developing broadband services based on ML-IP and are gaining many new subscribers. A leading example is a Canadian service provider - Radiant Communications. They offer the 'custom branded' TurboDSL service to businesses. It is based on multiples of their 2.5M/800K ADSL service aggregated by ML-IP from the subscriber into their network. For more details about how they have positioned the TurboDSL service simply click on the link below.
http://www.radiant.net/turbodsl.cfm
Call us today to discuss how you can create an ML-IP powered broadband service within your network and enable a wide range of subscribers to incrementally improve their broadband speed and reliability. ePipe engineers are available to discuss your network configuration, ML-IP evaluation program and technical training needs.
http://www.ml-ip.com/html/corporate/corpaddress.html
Below are ePipe publications that will help you to position the benefits of your 'custom branded' ML-IP broadband solution to your subscribers.
http://www.ml-ip.com/html/solutions/mlip-intro.html
http://www.ml-ip.com/html/solutions/providers-bandwidth.html
http://www.ml-ip.com/html/solutions/mlip-business-proposition.html
| ADSL | Asymmetrical DSL (higher rate downstream than upstream) |
| ATM | Asynchronous Transfer Mode |
| Bandwidth | The capacity of a given transmission channel (usually in bits per second) |
| CBD | Central Business District |
| CPE | Customer Premises Equipment |
| DSL | Digital Subscriber Line; broadband data service |
| DMT | (Discrete Multi-tone) - the leading method of signal modulation for DSL |
| Ethernet | A network protocol used to connect multiple devices within a network
at 10, 100 or 1,000 Mbps |
| Frame Relay | A packet-switching protocol for connecting devices across a Wide Area Network, typically over copper wire (T1) |
| G.DMT | a form of ADSL that uses discrete multi-tone technology with a splitter |
| G.Lite | (also known as DSL Lite, splitter less ADSL, and Universal ADSL) - a slower ADSL |
| ISDN | Integrated Services Digital Network; transmits data at 64 or 128Kbps over copper wire |
| IP | Internet Protocol |
| ISP | Internet Service Provider – the vendor that provides access to the Internet |
| ML-IP | Multilink IP combines bandwidth of links end to end through a switched network |
| PSTN | Public Switched Telephone Network |
| SHDSL, SDSL | Symmetrical DSL – equivalent upstream and downstream data rates |
| VDSL | Very High Speed Digital Subscriber Line |
| VPN | Virtual Private Network |
INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT (referred to as an Application Note) IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND BY EPIPE, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. The user assumes the entire risk as to the accuracy and the use of this Application Note. This Application Note may be copied and distributed subject to the following conditions: 1) All text must be copied without modification and
all pages must be included. Copyright © 2003 ePipe Pty. Ltd. All Rights are Reserved. For further information, contact ePipe by sending email to support@ml-ip.com, quoting the name of this paper in the subject header. |
|
Document Number: |
First Edition: October, 2002 |
![]()
about ePipe | products | solutions | support | information center | contact us
Copyright © 2002 ePipe Pty. Ltd. All rights reserved.